Leave Your Message
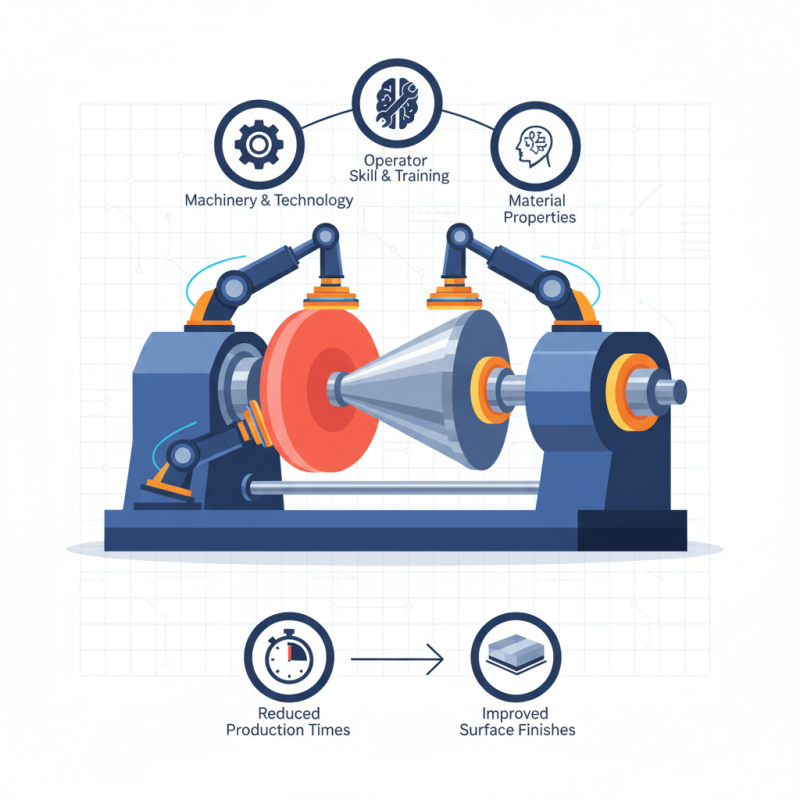
In the realm of modern manufacturing, mastering the Spinning Metal Process is crucial for producing high-quality metal components efficiently. This innovative technique, which involves the deformation of a metal disc into a desired shape through rotational force, has gained prominence due to its ability to create complex geometries while minimizing material waste. Industry expert Dr. Emily Sanders emphasizes the importance of precision in this process, stating, "The success of any metal spinning project hinges on the operator's skill and familiarity with the machinery, as well as a deep understanding of material properties."
As manufacturers seek to enhance their competitiveness, the Spinning Metal Process presents numerous advantages, including reduced production times and improved surface finishes. However, achieving mastery in this technique requires not only technical know-how but also an appreciation of the nuances involved in the manipulation of various metals. By embracing a holistic approach that combines training, technology, and continuous improvement, manufacturers can harness the full potential of the Spinning Metal Process, ultimately leading to innovative product designs and optimized production lines.
Through this guide, we aim to provide essential tips for mastering the Spinning Metal Process, drawing from both expert insights and practical experience to equip manufacturers with the knowledge necessary for success in this dynamic field.
The spinning metal process in manufacturing is a vital technique used to create cylindrical parts from sheet metal. This process involves the rotation of a metal blank, which is then shaped by a tool applied against it, allowing for precise and uniform thickness across the entire component. Common materials suitable for spinning include aluminum, brass, and stainless steel. Due to its ability to produce complex geometries and lightweight structures, spinning is widely used in industries such as automotive, aerospace, and HVAC systems.
As manufacturers seek to enhance efficiency and product quality, understanding the intricacies of the spinning metal process becomes essential. Factors such as the type of tooling, rotation speed, and feed rate play critical roles in determining the final product's quality. Properly selecting these parameters, along with implementing robust quality control measures, ensures a high level of precision while minimizing material waste. Additionally, advancements in computer-aided design (CAD) and simulation technologies have revolutionized how manufacturers approach the spinning process, allowing for better planning and execution of complex designs.
Metal spinning is a versatile manufacturing process that involves rotating a metal disc or blank to form it into a desired shape. Understanding the key materials used in metal spinning is essential for achieving high-quality results. Commonly used materials include aluminum, brass, and stainless steel. Aluminum is favored for its lightweight nature and excellent formability, making it ideal for intricate designs. Brass, known for its appealing finish and corrosion resistance, is often employed in decorative applications. Stainless steel offers durability and strength, which is crucial for components subjected to high stress.
When mastering the metal spinning process, consider these essential tips: first, select the appropriate material based on the part's application and required properties. Second, ensure optimal tooling and machine settings to minimize defects during spinning. Research indicates that advancements in materials, such as emerging ferromagnetic materials, could further enhance the efficiency and performance of the spinning process, opening up new possibilities for semiconductor spintronics and electronic component manufacturing. These innovative materials can reduce production costs while improving the end product's functionality.
Incorporating cutting-edge materials and methods is vital in staying competitive in the manufacturing landscape. As industry reports highlight, leveraging sustainable practices and efficient material usage will lead to significant advancements in product quality and environmental impact.
Preparing for metal spinning is a crucial step in ensuring a successful outcome in the manufacturing process. The first tip is to select the right material for your project. Different metals have unique properties that can affect spinning performance. For example, aluminum is a popular choice due to its lightweight and malleable nature, making it easier to shape. Always consider the thickness and diameter required, as these factors will influence both the material choice and the spinning technique.
Next, it's essential to have the right tools and equipment ready. A spinning lathe is fundamental, but don’t overlook other tools like mandrels, which can assist in achieving precise shapes. Before starting, perform a thorough inspection of your equipment to ensure it is functioning correctly and safely. Finally, preparing a detailed plan or design can streamline the process. This includes sketches and calculations, which will help you visualize the final product and identify potential challenges early on. Effective preparation not only enhances efficiency but also elevates the quality of the final spun metal product.
| Tip | Description | Importance Level | Tools Required |
|---|---|---|---|
| Material Selection | Choose the right metal type based on thermal and mechanical properties. | High | Material samples, specifications sheet |
| Tooling Design | Design the tooling considering the final shape and precision requirements. | High | CAD software, prototyping materials |
| Machine Setup | Calibrate the spinning machine for optimal RPM and pressure. | Medium | Digital caliper, RPM gauge |
| Trial Runs | Conduct trial runs to fine-tune the parameters. | Medium | Test pieces, inspection tools |
| Quality Control | Implement a strict quality control process for the finished product. | High | Measuring instruments, quality checklist |
 Mastering the spinning metal process requires an in-depth understanding of various techniques to ensure precision throughout production. One key approach involves maintaining the right material properties. Selecting the appropriate metal with the correct thickness, ductility, and tensile strength is crucial. A well-chosen material not only withstands the stresses of spinning but also allows for achieving desired shapes and tolerances effectively.
Mastering the spinning metal process requires an in-depth understanding of various techniques to ensure precision throughout production. One key approach involves maintaining the right material properties. Selecting the appropriate metal with the correct thickness, ductility, and tensile strength is crucial. A well-chosen material not only withstands the stresses of spinning but also allows for achieving desired shapes and tolerances effectively.
Another essential technique is the control of spindle speed and feed rates. Optimizing these parameters can profoundly impact the surface finish and dimensional accuracy of the final product. High spindle speeds combined with appropriate feed rates enable smooth operation and reduce the likelihood of defects such as warping or uneven thickness. Additionally, employing advanced tooling—specifically designed for the spinning process—can significantly enhance precision. Tools with sharp cutting edges and proper profiles facilitate better material flow and help achieve intricate designs, which are vital in modern manufacturing applications.

Metal spinning is a highly efficient manufacturing process, but it comes with its own set of challenges that can impact production quality and efficiency. One common challenge is achieving the desired wall thickness. Variability in the spinning process can lead to uneven formation, harming the structural integrity of the final product. To mitigate this, manufacturers should employ consistent control over the spinning speed and feed rate, ensuring uniform material distribution.
Another significant issue faced in metal spinning is tool wear. As tools come into constant contact with the spinning metal, they can quickly degrade, leading to increased production costs and downtime. Implementing regular tool maintenance and using high-performance materials for tooling can greatly extend tool life and improve overall process reliability. Additionally, conducting routine inspections allows manufacturers to promptly address wear, ensuring that quality standards are consistently met.